OpenShift is a powerful Kubernetes-based platform for deploying and managing applications. If you’re just getting started, Red Hat OpenShift Local (previously CodeReady Containers –CRC) is a quickest way to run a local and single node OpenShift cluster on your laptop or VM. In this guide, we’ll walk through installing OpenShift Local, deploying a sample Node.js app, connecting it to a PostgreSQL database, and exploring scaling options.
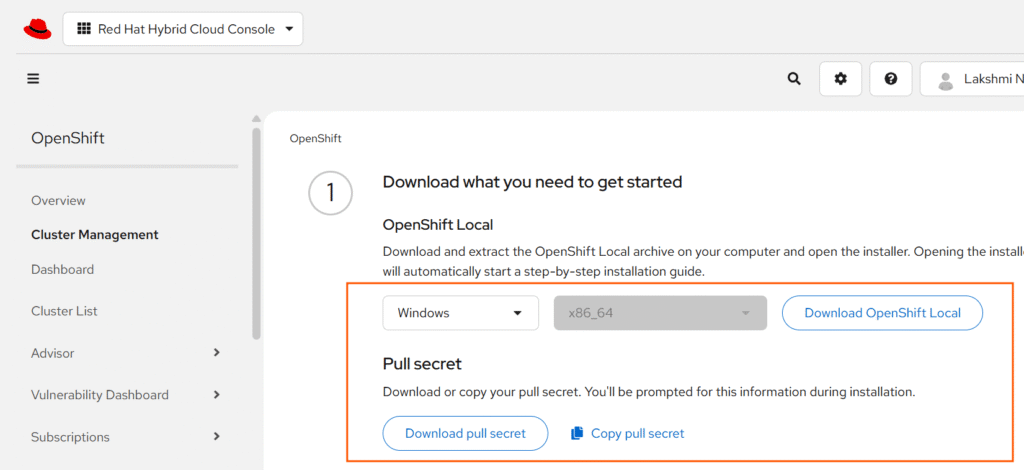
1. Download the OpenShift Local installer for Windows from Red Hat’s developer portal: Download here.
Note: I have done this in a laptop with 32GB RAM, 16CPU, and 200 GB SSD, Windows 11.
requirements:
CPU: Recent Intel processor with at least 4 physical cores (Apple Silicon Macs are supported).
Memory (RAM):
-- Minimum: 16 GB
-- Recommended: 32 GB (to comfortably run applications along with OpenShift Local).
Disk Space: At least 35 GB free for installation.
OS:
Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (version 1709) or later.
macOS 11 Big Sur or later.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Fedora, or CentOS 8 or later.2. Download the pull secret and save it in a text file for later use.
3. Extract the downloaded file “crc-windows-installer.zip” and install the application by
following the wizard.
4. Open a command prompt as non admin user (if you have no non-admin user, please
create one), In cmd prompt, type command “crc setup”.
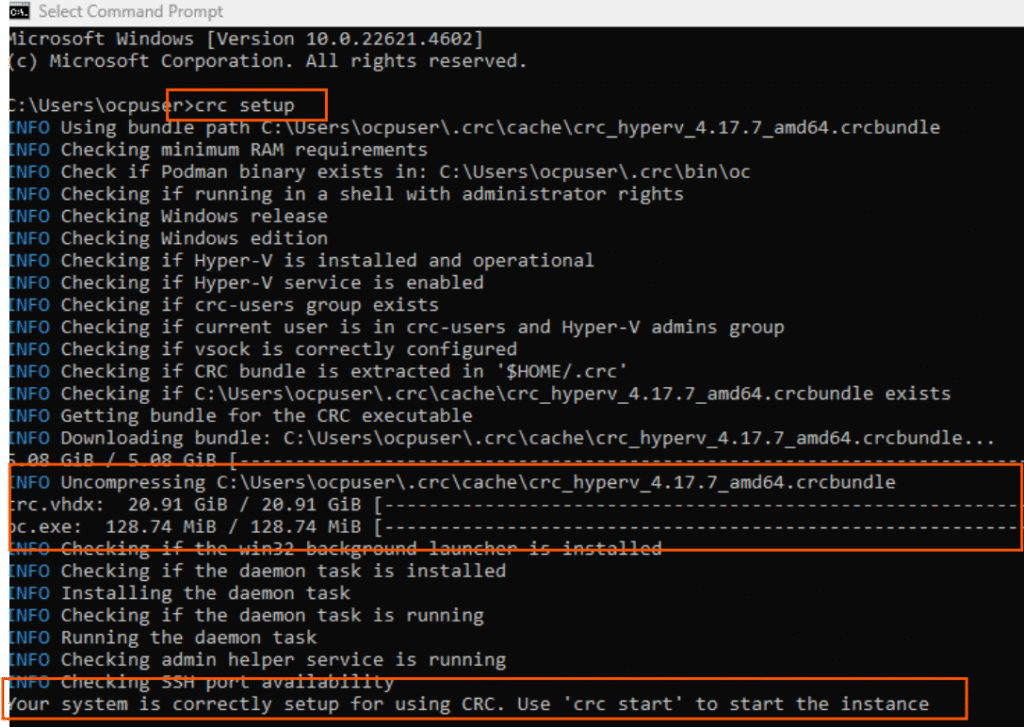
you can see in the screenshot, it downloads the crc.vhdx (hyperv disk file) and
validates other things for the next step. Once the setup completes, you can see it asks to use a command “crc start” to start the crc instance.
5. After you run crc start command, you can see that it started spinning up Hyper VM.
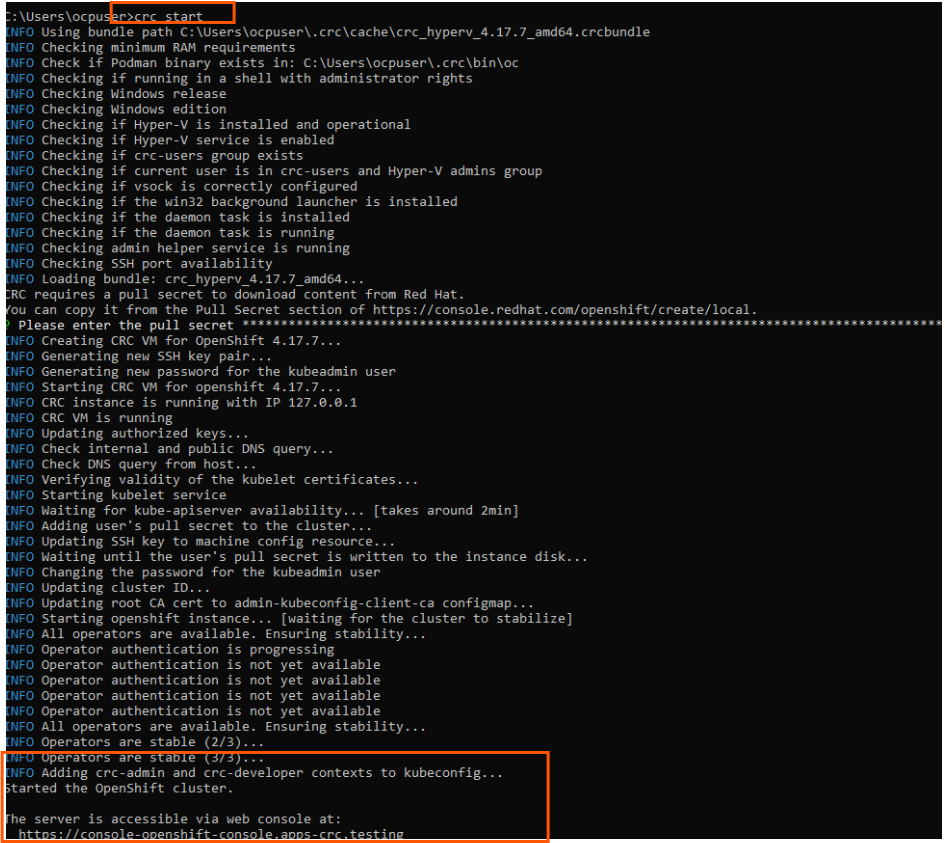
Once all the steps completed, you can see it provided the openshift cluster details,
admin and developer user details.
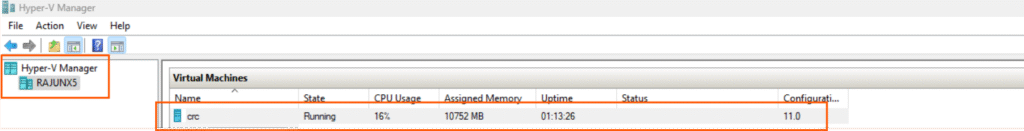
You can check in HyperV Manager to see the CRC VM is up and running.
6. Now we can login to our openshift local cluster using the console URL shown from the output of crc start command (refer previous screenshot)., which is running locally on yourVM/Laptop and we can deploy an application for testing.
7. We will download the oc command line tool, we will use oc to interact with our openshift cluster in commandline.
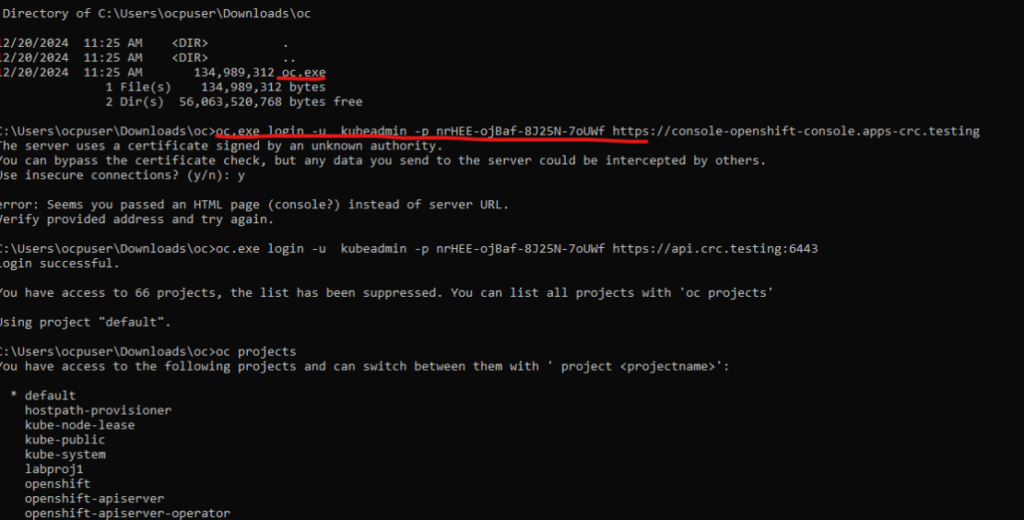
8. In openshift, the project is like the namespace in K8s. Before we start creating applications, we created a project called “labproj1”, In this project we will deploy our applications.
Deploy an application in OpenShift
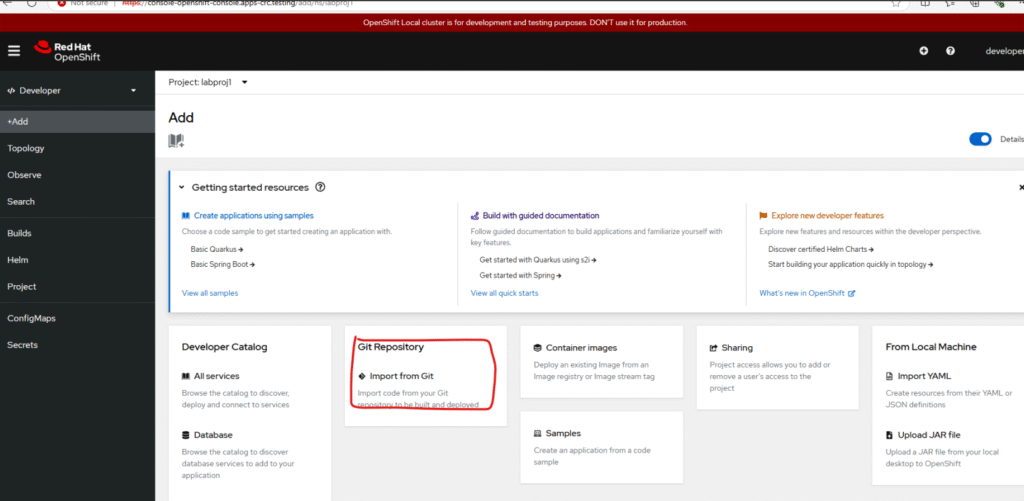
1. Login as developer, go to Topology, select your project ‘labproj1’ from dropdown.
2. As we don’t have any applications, we will click on the “Add Page” link to create our first application in OpenShift. We can deploy our application in several different ways here, we will use git repo.
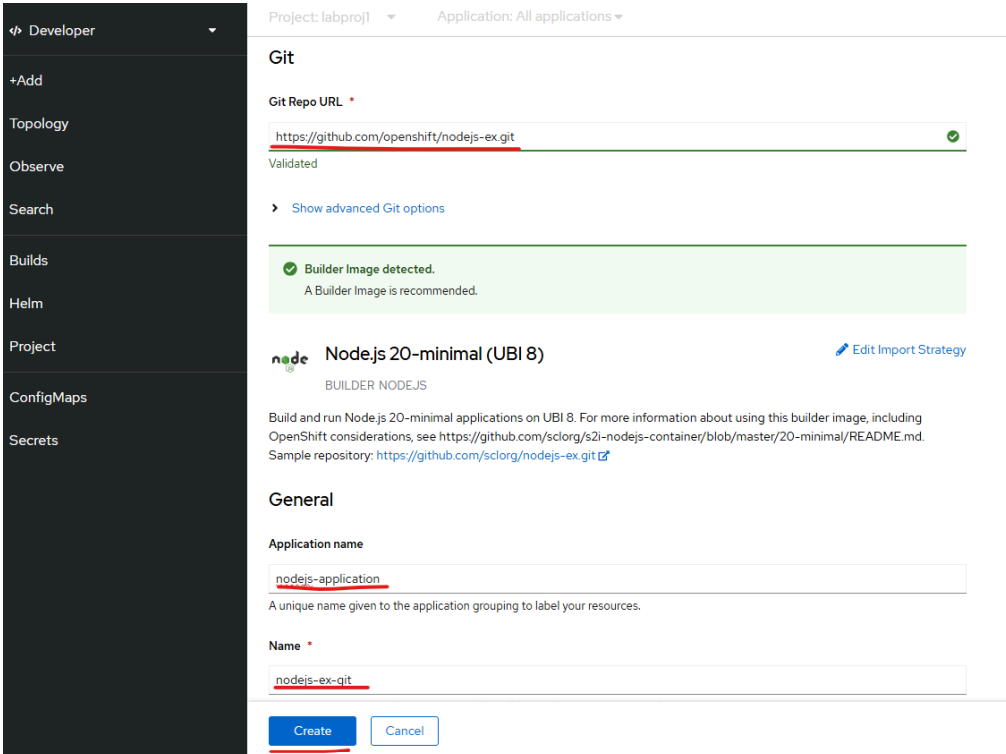
Provide the git URL and fill in the application name and other details, click on Create
button to create your app
We used this public github URL https://github.com/openshift/nodejs-ex.git for our
learning.
you can expose the application in advanced options while creating app.

Now our app is deployed, we can see its route details.

Click on the link in the Routes section to view your nodejs application in your browser.
3. Now lets prepare a psql db. This time, we will use the command line to create a psql db app. OpenShift provides an easy way to deploy PostgreSQL using an official template.
We will use it to set up our database.
oc new-app postgresql-persistent -p POSTGRESQL_USER=developer -p POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=developer -p POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=devdb --name=fruits-psql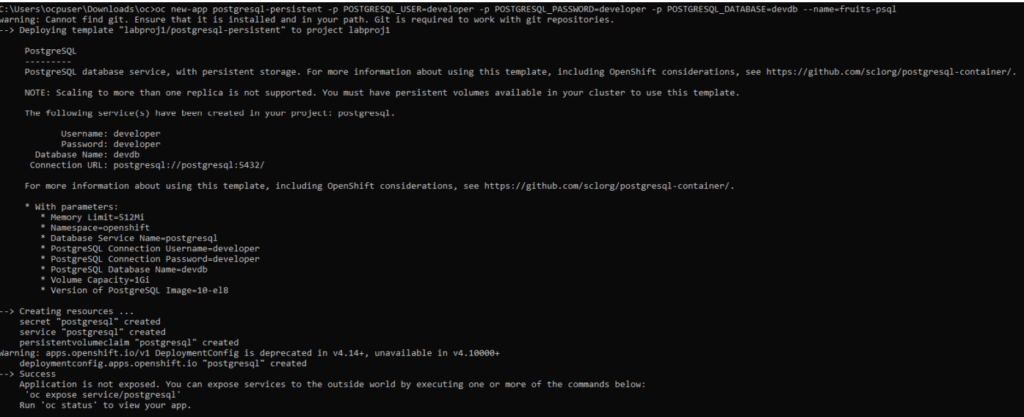
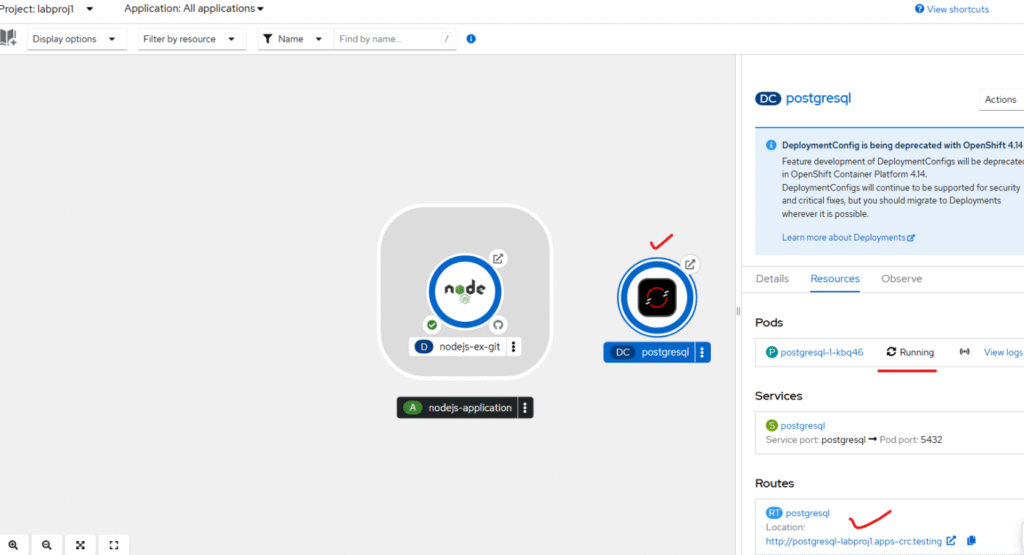
We can see the psql db deployed successfully, we can see service is exposed and it has persistent storage.
4. Next, we’ll configure the Node.js app to connect to the PostgreSQL database. This is
done by setting environment variables for the app deployment.
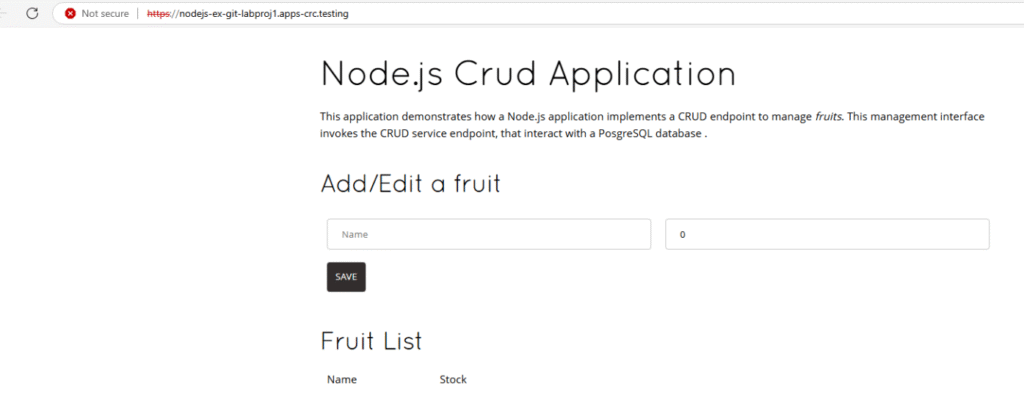
C:\Users\ocpuser\Downloads\oc>oc set env deployment/nodejs-ex-git POSTGRESQL_USER=developer POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD=developer POSTGRESQL_DATABASE=devdb POSTGRESQL_HOST=postgresql POSTGRESQL_PORT=5432 deployment.apps/nodejs-ex-git updated5. Once this db is connected, we can access our nodejs application and enter new fruit
details, edit/remove existing fruit entries and observe the changes in database.
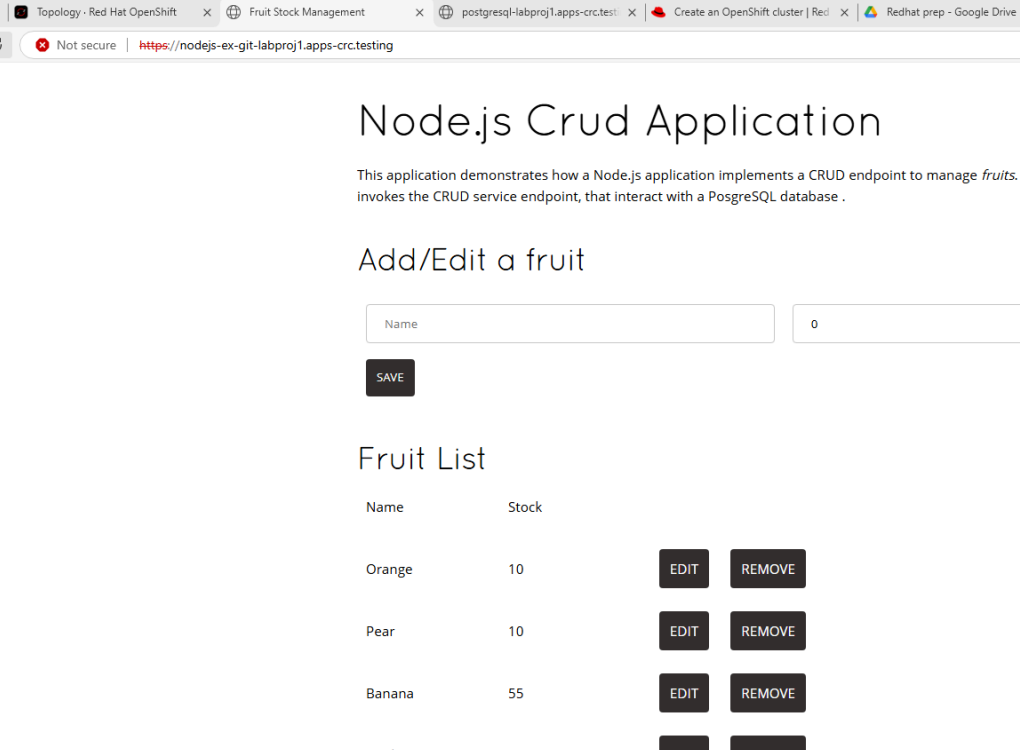
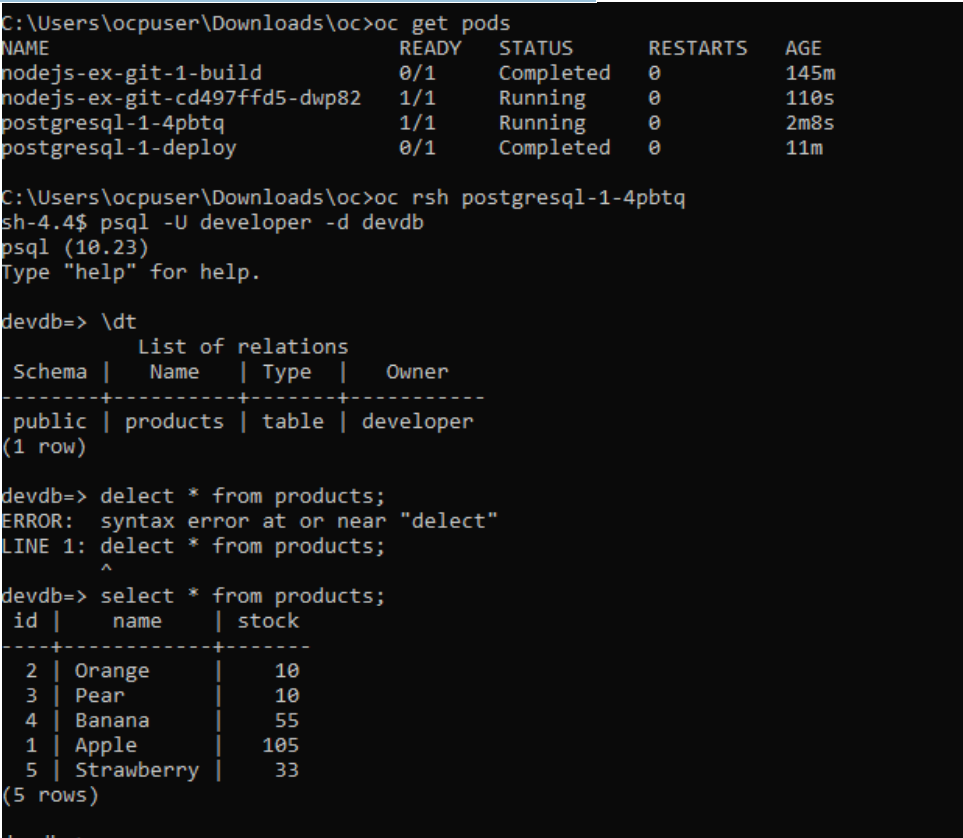
We can login the DB and check the table being updated
Summary
In this guide, we set up Red Hat OpenShift Local, deployed a Node.js app, connected it to a PostgreSQL database, This hands-on approach gives you a real feel for how OpenShift manages applications and databases in a Kubernetes-native way.